Background and Context
Toronto's Yellowbelt and Zoning By-Law
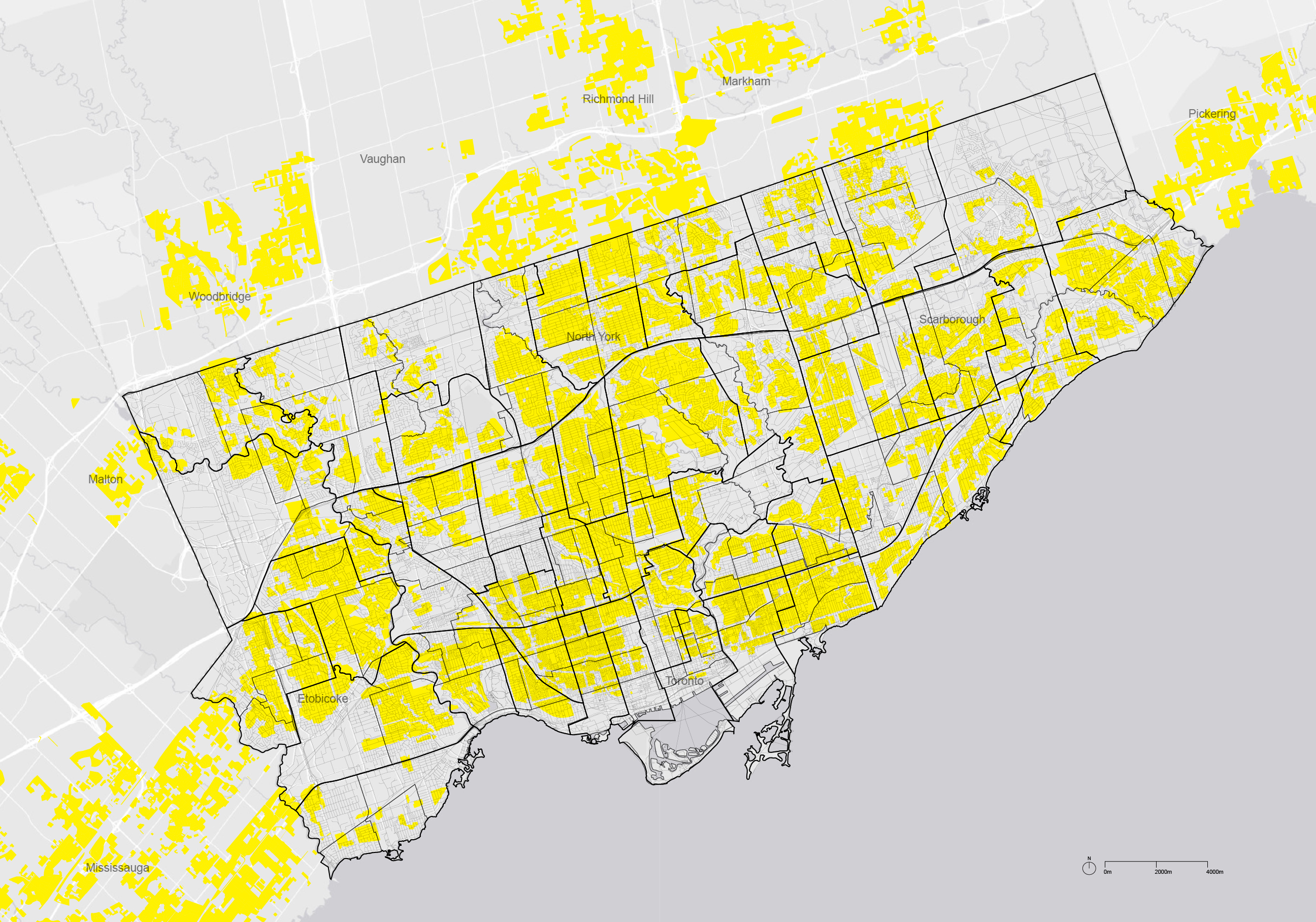
The term ‘yellowbelt’, created by Gil Meslin, an urban planner based in Toronto,
describes the vast areas of land in the Greater Toronto Area that is designated as neighborhoods.
The primary zone within the Yellowbelt is the Residential Detached (RD) zone,
which is specified in the city of Toronto's Zoning By-Law as zones that prohibit
higher-density construction (via a maximum height of 10 meters) and allow only single detached residential housing.
The yellowbelt often encompasses older, established neighborhoods with existing housing stock.
Zoning regulations, heritage sites, and other planning policies in place
play together to limit the density or type of development allowed.
The Current Housing Landscape in Toronto
The City of Toronto is now undergoing a well-known housing crisis, as the price of housing soars and the city strives to build more expensive condominium development in its designated areas for growth such as the downtown core, the majority of regional land supply remains off limits. The vast areas of detached homes that cover most of the land provide its lowest densities for housing and are protected from change.
The ‘Missing Middle’ Dilemma
Recognizing this imbalance in the housing market, the concept of ‘Missing Middle’ has emerged to provide insights and solutions to the housing affordability crisis in many North American cities. The Missing Middle refers to a range of housing types that are often absent or underrepresented between traditional single-family homes and large apartment buildings, including multiplex, townhouses, courtyard apartments, and other types of medium-density housing.
Addressing the Imbalance Through Mapping
In this web map, our objective is to shed light on Toronto's building footprint and Zoning By-Law, particularly focusing on the building height restrictions entrenched within the yellowbelt. Our aim is to bring attention to the inherent imbalances in the housing market, targeting key stakeholders such as city officials, urban planners, newcomers to the city, and residents seeking affordable housing solutions.